optical polarimeter uses|polarimeter calculation : Brand manufacturer Polarization by reflection was discovered in 1808 by Étienne-Louis Malus (1775–1812). See more webAbout This Content. You can run, but you can’t hide.. Enter the ruins of Freddy Fazbear’s Mega Pizzaplex in the FREE story DLC for Five Nights at Freddy’s: Security Breach! Gregory is once again trapped in the now .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Maryland, também chamada de Marilândia em português, é um dos 50 estados dos Estados Unidos, localizado na região nordeste do país. Maryland foi nomeada em homenagem à rainha Henriqueta Maria, francesa, esposa do rei Carlos I da Inglaterra. Maryland foi uma das treze colônias que rebelaram-se contra o domínio britânico na região. O cognome do estado é Old Line State, em homenagem às suas "tropas de linha" (troops of the li.
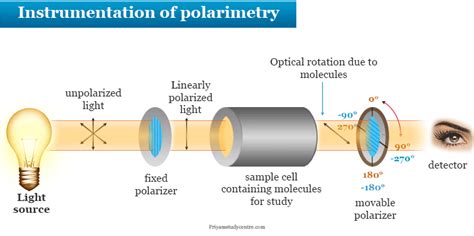
A polarimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure optical rotation: the angle of rotation caused by passing linearly polarized light through an optically active substance. Some chemical substances are optically active, and linearly polarized (uni-directional) light will rotate either to the left (counter . See morePolarization by reflection was discovered in 1808 by Étienne-Louis Malus (1775–1812). See moreThe polarimeter is made up of two Nicol prisms (the polarizer and analyzer). The polarizer is fixed and the analyzer can be rotated. The prisms . See more
Laurent's half-shade polarimeterWhen plane-polarised light passes through some crystals, the velocity of left-polarized light is different from that of the right-polarized light, thus the crystals are said to have two refractive indices, i.e. double refracting. See moreTraditionally, a sucrose solution with a defined concentration was used to calibrate polarimeters relating the amount of sugar molecules to the light polarization rotation. The International Commission for Uniform Methods of Sugar Analysis (ICUMSA) played a . See moreThe ratio, the purity, and the concentration of two enantiomers can be measured via polarimetry. Enantiomers are characterized by their property to rotate the plane of See morePolarimeters measure this by passing monochromatic light through the first of two polarising plates, creating a polarized beam. This first plate . See more
The angle of rotation of an optically active substance can be affected by:• Concentration of the sample• Wavelength of light passing through the sample (generally, . See moreA polarimeter is an optical instrument with which one can accurately measure the angle by which the polarization of light is rotated e.g. when it passes through an optically active medium (containing chiral molecules).Generally, the observed optical rotation at 436nm is approximately double and at 365nm about three times that at 589nm. Polarimeter Light Sources. It is now common practice to use other light sources such as xenon or tungsten halogen. Automatic Polarimeter: This type of polarimeter uses a digital display to measure the degree of polarization. It is commonly used in pharmaceuticals and chemistry. Polarimeter Spectrometer: This type of polarimeter is used to measure the optical activity of a sample over a wide range of wavelengths. It is commonly used in physics and chemistry.
An easily constructed and inexpensive polarimeter with an optical rotation angle resolution of about 0.5° is presented. It is made from small pieces of polarizing film, 2 LEDs, a protractor, and a few wires, all held in .In addition, the Autopol IV has an accuracy of 0.002 for Optical Rotations of 1°Arc for a total unknown of +/-0.002 under the same conditions: AUTOPOL II – Education Polarimeter. The AUTOPOL II Automatic Polarimeter is a general-purpose polarimeter with ±0.01 Degrees Optical Rotation accuracy. This accuracy is applicable for food .
Optical Instruments. M. de Angelis, G.M. Tino, in Encyclopedia of Condensed Matter Physics, 2005 Polarimeter. Polarimeters are optical instruments used for determining the polarization properties of light beams and samples. Light-measuring polarimeters determine the polarization state of a beam of light and give its polarization characteristics.In a polarimeter (figure 2), plane-polarized light is introduced to a tube (typically 10 cm in length, figure 3) containing a solution with the substance to be measured. . As mentioned earlier, polarimetry can be used to determine optical purity of enantiomers. Example 2: The observed specific optical rotation of a compound is [α]= +7.00 o .If an optical active substance is in a sample tube, the analyzer is rotated until the original dark condition is restored. The rotation is observed by looking through the analyzer, and is identified by a change in intensity of illumination. . The polarimeter uses a light source, usually a mercury or sodium discharge tube. There are several .
Step-by-Step Guide on Using a Polarimeter. Operating a polarimeter correctly is critical to obtaining precise and accurate measurements. Whether you are using a manual, digital, or automatic polarimeter, following a structured, detailed process ensures consistent results. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to use a polarimeter effectively. The polarimeter’s ease of use, compact size, fast measurement times and high angular resolution make it a capable and versatile tool for analytical science, while its low cost means it is .Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it travels through certain materials. Circular birefringence and circular dichroism are the manifestations of optical activity.Optical activity occurs only in chiral materials, those lacking .
Measurement of Optical Rotation . Polarimeter is the instrument that measures the direction and angles of rotation of plane-polarized light. The plane-polarized light pass through the sample tube containing the solution of sample, and the angle of rotations will be received and recorded by the analyzer, as summarized in Fig. 5.4c.. Figure 5.4c Measurement of Optical .
The automatic polarimeter, a critical equipment for detecting optical rotation, is used in a variety of industries, including pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and chemical analysis.This article delves into the operation, functioning, uses, and benefits of automatic polarimeters in the realm of analytical science.Polarimetry is used in remote sensing applications, such as planetary science, astronomy, . A polarimeter is the basic scientific instrument used to make these measurements, . such as is done in polarimetric synthetic aperture radar. Polarimetry can be used to measure various optical properties of a material, including linear birefringence, .
In a polarimeter (figure 2), plane-polarized light is introduced to a tube (typically 10 cm in length, figure 3) containing a solution with the substance to be measured. . As mentioned earlier, polarimetry can be used to determine optical purity of enantiomers. Example 2: The observed specific optical rotation of a compound is [α]= +7.00 o .
Digital polarimeters are a type of polarimeter that uses digital technology to measure the optical rotation of a substance. Digital polarimeters are typically more accurate than manual polarimeters and are often used in .Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The effect of path length on optical rotation. The longer the path of light through a solution of molecules, the more molecules will be encountered by the light, and the greater the optical rotation. The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample. In summary:A polarimeter is a device that measures the rotation of linearly polarized light by an optically active sample. This is of interest to organic chemists because it enables differentiation between optically active stereoisomers, i.e., .
t spot blood test bottle
Optical activity is one of the few ways to distinguish between enantiomers. A . The plane of polarization can be determined by an instrument called a polarimeter, shown in the diagram below. Monochromatic (single wavelength) light, is polarized by a fixed polarizer next to the light source. A sample cell holder is located in line with the . Using a Polarimeter and a demonstration of the physical phenomenon underpinning the technique. Using the polarimeter 1:45Demonstrating polarimetry with a las. Let’s dive into the history and importance of these forgotten centers of optical research. Lost Mechanical Polarimeter Labs of Jena. Jena, a city in Germany, has a rich history in optics and precision instruments. Among its many contributions to science, the mechanical polarimeter labs stand out. These labs, once bustling with activity, are .
Understanding the Basics of a Polarimeter. A polarimeter is a device that detects the rotation of plane-polarized light as it passes through an optically active substance. This substance could be in the form of a liquid, a solid, or a solution. The degree of rotation is proportional to the optically active compound concentration and the length of the sample tube.Recording optical rotation with a polarimeter: The plane of polarisation of plane polarised light (4) rotates (6) as it passes through an optically active sample (5).This angle is determined with a rotatable polarizing filter (7).. In chemistry, specific rotation ([α]) is a property of a chiral chemical compound. [1]: 244 It is defined as the change in orientation of monochromatic plane .The resulting filtered solution's optical rotation is measured in the polarimeter and used to calculate percent starch; a similar optical procedure uses hydrochloric acid and a saturated lead solution. More recently developed methods of starch analysis, however, usually rely on the ability of the enzymes alpha-amylase and amyloglucosidase to . Optical activity is measured by a polarimeter, and is dependent on several factors: concentration of the sample, temperature, length of the sample tube or cell, and wavelength of the light passing through the sample. Rotation is given in +/- degrees, depending on whether the sample has d- (positive) or l- (negative) enantiomers. .
A model for optical rotation L. L. Jones and Henry Eyring Journal of Chemical Education 1961, 38 (12), 601 DOI: 10.1021/ed038p601 For those interested in the physics or theoretical underpinnings of the phenomenon of optical rotation, this paper by Prof. Henry Eyring (the same of Eyring equation fame) is a very good read. Optical rotationAsk the Chatbot a Question Ask the Chatbot a Question polarimetry, in analytic chemistry, measurement of the angle of rotation of the plane of polarized light (that is, a beam of light in which the vibrations of the electromagnetic waves are confined to one plane) that results upon its passage through certain transparent materials. Polarimetry is of interest to the chemist .Optical Activity Laboratory Organic Chemistry Lab: AEMoody This laboratory will introduce you to basic principles of optical activity and the use of a simple polarimeter; for example, the relationship of the specific rotation, [α], of a molecule to its concentration, c (units: g/mL), in solution and the pathlength, l (units: dm), of the .
what does a polarimeter do
schematic diagram of polarimeter
Aconchegante Hostel em Diadema Galeria 124, experimente uma estadia memorável e única em nosso espaço, onde o ambiente vintage e hospitalidade se unem para criar uma atmosfera inspiradora. Localizado no coração da cidade, o nosso hostel está preparado para receber você no conforto e aconchego de um lar.
optical polarimeter uses|polarimeter calculation